An ileostomy is when an opening is made in the small intestine through the stomach. In ileostomies, your stool is eliminated practically all day long and these are usually liquid (with a more yellowish colour) or have a porridge-like consistency, as they have not been able to pass through the large intestine properly (where water is absorbed, and the stools harden). In addition, they contain digestive enzymes which can irritate the skin around the stoma.
The normal amount of passed stools (also called output) is between 500 and 1,000 ml per day, which corresponds to about one or two half-full stoma bags (depending on the type of bags used).
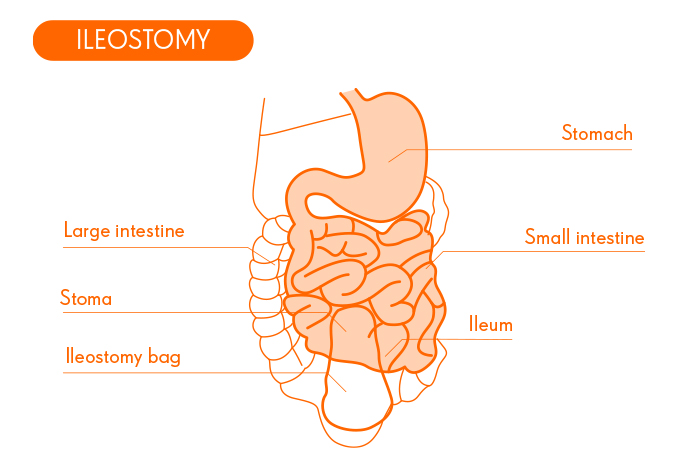
When the amount of passed stools is within these limits, the ileostomy is considered normal-functioning, and a low-fibre diet is recommended, whilst keeping an eye out for foods that stimulate bowel movement; use light cooking methods and low-fat and ensure adequate water intake.
When the amount of passed stool is greater than 1.5 litres per day (3-4 bags per day) it is considered a high output ileostomy and a diet very low in fibre and foods that stimulate bowel movements, using low-fat and light cooking and adequate water intake is recommended.
WHAT DO WE RECOMMEND?
Eat in a relaxed environment, keeping your mouth closed and chewing well to avoid excessive formation of gas and large bits of food coming out of the ostomy (chewing too little increases the risk of obstruction).
Fasting or skipping meals increases the elimination of liquid stools and gas.
This may interfere with the proper fit of the pouching plate.
Being an ileostomy carrier entails a higher risk of dehydration, as a daily volume of fluids and minerals are lost through the ostomy that would normally be reabsorbed in the colon. For losses of more than 1.5 l/day, follow the recommendations for diarrhoea and make sure to keep well hydrated: drink water, isotonic drinks (with low sugar content) or oral saline, strained fruit juices, smoothies, or herbal teas frequently, but in small sips and preferably in between meals, so as not to confuse the texture of the stool after eating. Limit peristalsis-stimulating drinks (coffee, unstrained juice) and take rehydration drinks. Homemade jellies are also a good option to stay hydrated.
| Recommended drinks in case of elevated loss through the ileostomy | ||
|
After surgery, it is advisable to test your tolerance to lactose gradually. Start with a low-lactose diet, based on lactose-free milk and fresh or Cottage cheese and fermented derivatives, such as yoghurt or hard cheese (already low in lactose). If these foods are well tolerated and ostomy output does not increase, lactose-containing dairy products can be gradually incorporated, starting with cheeses and yoghurts, and finally milk, in small quantities.
In the case of high-output ileostomy (more than 1.5 l/day or 3-4 stoma bags), follow a very low-fibre diet, with foods that do not stimulate bowel movements, using low-fat and light cooking.
| Example menu plan in case of high output ileostomy | ||||||||||||||||
|
In the case of a normal-functioning ileostomy (less than 1.5 litres of output or 1-2 bags per day), follow a low-fibre diet, with foods that do not stimulate bowel movement, using low-fat, lightly cooked foods. Tolerance to pulses is very variable, so eat them occasionally, always choosing pulses without skin and always mashed. If well tolerated they can also be eaten without mashing but keeping in mind the importance of chewing the pulses well and mixing them with cereals (rice, noodles…) or tubers (potato).
| Menu example plan in case of normal-functioning ileostomy | |||||||||||||||
|
Restricting and/or moderating the consumption of fibre-rich foods.
| Foods allowed and not advised in the diet low in moderate fiber | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
It is important to know which foods can cause constipation, diarrhoea, flatulence, or changes in the colour of your stool so that adjustments can be made quickly to remedy the different situations.
When having an ostomy, the intake of certain foods or changes in diet can lead to modifications.
It is important to gradually introduce foods and methods of preparations to assess their effect and tolerance. Individual tolerance to each food can be very different. Symptoms that may indicate poor tolerance are nausea, vomiting, bloating or increased liquid bowel movements through the ostomy. A good alternative is to use a food diary.
| Situations and foods to consider when having an ostomy | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||






